
Our Energy Future: Green Ammonia
Read time: 2 minutes
Green ammonia is a diverse gas with applications to agriculture and renewable energy. Here, we take a deep dive into the world of green ammonia, uncovering its potential for a clean energy future and the barriers it currently faces.
Ammonia (NH3) is a pungent, colourless gas widely used in the production of fertilisers and industrial chemicals. Unlike ammonia, known as grey ammonia, green ammonia does not emit CO2 in its production process. Presently, grey ammonia emits roughly 2 tonnes of CO2 for every tonne produced, and the current market volume of ammonia is 185 million tonnes a year. In total, global ammonia production contributes 1.8 per cent to global CO2 emissions.
Currently, the most common technique of ammonia production is steam methane reforming (SMR) which involves the use of methane, water and air. Around 90 per cent of carbon dioxide produced as a by-product of ammonia stems from the SMR process. To increase the production and development of green ammonia, sustainable hydrogen is needed.
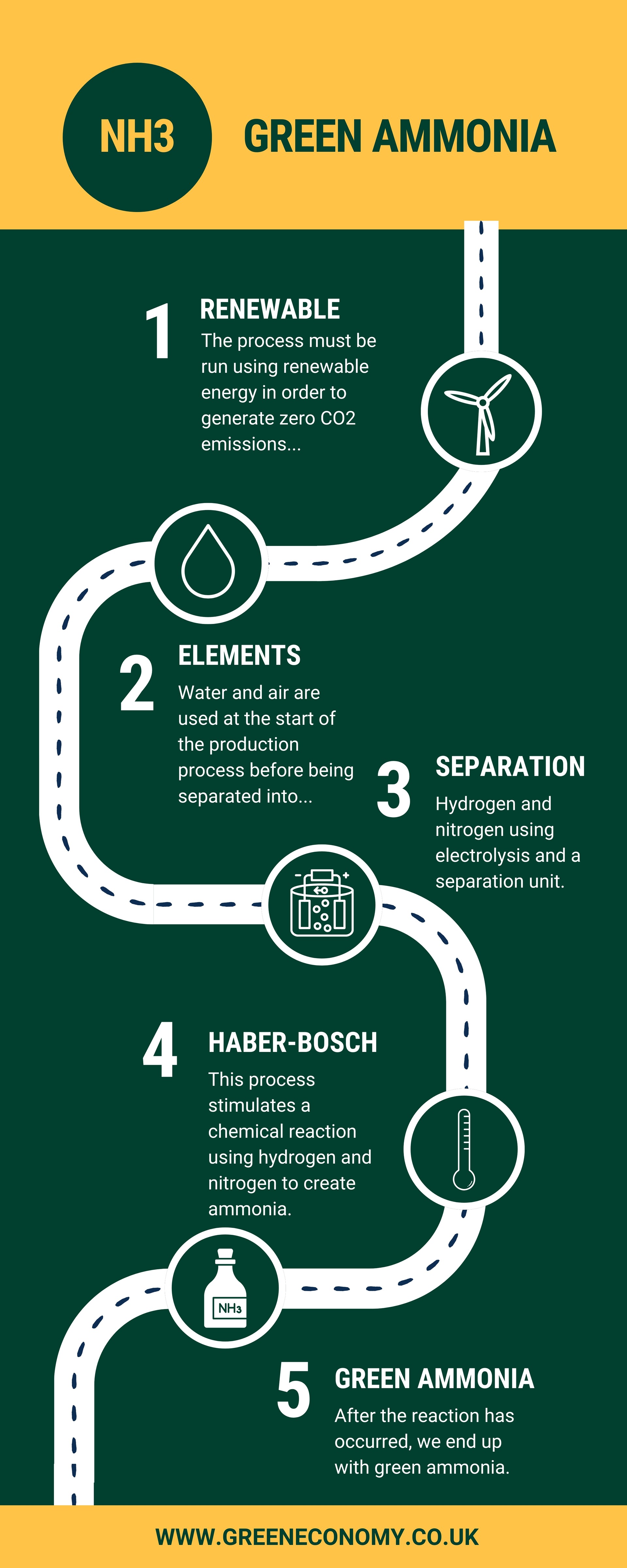
In order to make renewable, green ammonia, a process of electrolysis is used. Electrolysis involves separating green hydrogen from water and nitrogen from air and feeding these into the Haber-Bosch process which must be powered by renewable energy to maintain the carbon free label.
The Haber process is specifically designed for the production of ammonia and involves stimulating a chemical reaction using nitrogen and hydrogen at temperatures ranging from 400C – 450C at a pressure of 200 atmospheres. The reaction mixture is then cooled to create liquid ammonia which can be extracted.
Ammonia is being heralded as a low carbon solution for net zero and a sustainable energy future. Without being properly managed, ammonia could generate high levels of carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide, two prominent greenhouse gasses. Therefore, understanding the process of producing green ammonia and its most effective uses is essential for cutting emissions.
Much like the fossil fuels green ammonia could replace, it can be used as an energy carrier, a fuel source, and a fertiliser. At present, roughly 80 per cent of ammonia production goes into fertiliser for agricultural processes, with 20 per cent fed into industrial processes. Ammonia is a rich source of nitrogen which is essential for plant growth, making it an effective fertiliser. Without ammonia, and the technology which goes into producing it, the world’s population would be very different and facing extreme food scarcity.
Ammonia can also be burnt and used as a zero-carbon fuel. When burnt, the only by-products of ammonia are hydrogen and nitrogen. However, if not carried out effectively or to completion, ammonia’s combustion process may generate N2O, or nitrous oxide, which is a harmful gas.
Green ammonia is also being used as an energy vector, meaning it is considered an effective carrier and storage centre for hydrogen which has many practical, low carbon applications.
Interest in hydrogen as a zero-carbon fuel is growing rapidly, but hydrogen is notoriously difficult to store and transport. Ammonia is comparably easy to liquify, store and transport and, using the Haber-Bosch process, can later be used to separate hydrogen. Due to the widespread nature of ammonia in agriculture, a well-established system of transporting ammonia already exists, making it an ideal solution to hydrogen transport woes.
According to the RePowerEU plan from the European Commission, 20 million tonnes of renewable hydrogen will be required by 2030 to power local industry, and green ammonia is set to service a significant portion of this demand.

Do you install green technology or provide net zero services?
Green Economy's partners have new sales opportunities for installers of solar, LED lighting, heat pumps, EV charging and battery storage, and for providers of energy management systems.
Green technologies and services businesses can create a free profile on the Marketplace to receive direct enquiries from new customers, as well as exclusive sales opportunities from Green Economy.
Explore servicesSearch for a local, trusted green tech supplier
Search for local suppliers by technology, location and experience on the Green Economy Marketplace.
Need more help? We can help you navigate the journey to net zero with expert support and guidance.
Explore MarketplaceCollaborate, innovate and grow
Join our network to hear industry trends, network with peers and foster new partnerships.
Callum Henderson, Nemiah said:
“It was valuable event for us, we generated more leads this morning than we had done in an entire month!
Explore events calendar